Unveiling Students' Refractive Thinking Process Who Use a Single Strategy in Decision Making
Abstract
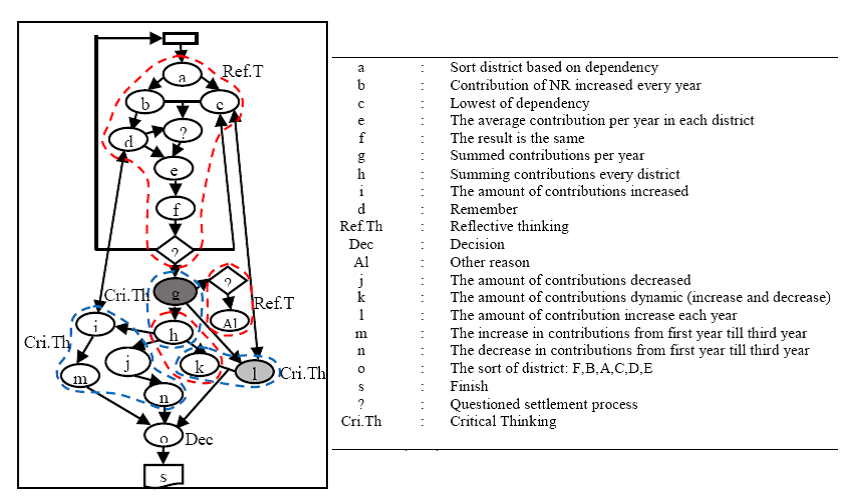
The thinking process characterized by reflective thinking towards critical thinking to produce a decision is called the refractive thinking process. However, how the refractive thinking process occurs in the subject needs to be revealed. This study aims to reveal the refractive thinking process in subjects who use a single strategy in decision making. This study is a qualitative approach involving 25 mathematics education students from two universities in Malang, East Java, Indonesia. Each student was given a test on the problem of ordering cities based on the level of dependence on the central government from lowest to highest. The decision to order cities was based on local revenues data that varied between cities and unstable from year to year. In this study, the researcher only analyzed the refractive thinking process of one subject who used a single strategy in decision making. The subject was asked to think aloud. The results showed that students who carried out the refractive thinking process with a single strategy only needed one alternative solution to make a decision, namely by summing up the contributions of each city per year. The subject only identified the comparison of the amount and increase in the contribution of each city as a consideration for making a decision.
Downloads
References
Asare, A. S. (2012). Reflective collaborative practices: What is the teachers’ thinking? A Ghana case. Creative Education, 3(4), 448-456. http://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2012.34069
Choy, S. C., & Oo, P. S. (2012). Reflective thinking and teaching practices: A precursor for incorporating critical thinking into the classroom?. International Journal of Instruction, 5(1), 167-182. https://www.e-iji.net/dosyalar/iji_2012_1_11.pdf
Colley, B. M., Billics, A. R., & Lerch, C. M. (2012). Reflection: A key component to thinking critically. The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 3(1), 1-19. http://doi.org/10.5206/cjsotl-rcacea.2012.1.2
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (Third edition). California: SAGE Publications.
Curcio, F. R. (2001). Developing Data-Graph Comprehension in Grade K-8 (Second edition). Reston: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics.
Dawe, G., Jucker, R., & Martin, S. (2005). Sustainable development in higher education: current practice and future developments: A report for the Higher Education Academy. Heslington: Higher Education Academy. https://www.sustainabilityexchange.ac.uk/files/sustdevinhefinalreport.pdf
Dewey, J. (1933). How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking and the educational process. New York: D.C. Heath & Co Publishers. https://bef632.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/dewey-how-we-think.pdf
Doerr, H. M., & English, L. D. (2003). A modeling perspective on students' mathematical reasoning about data. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 34(2), 110-136. https://doi.org/10.2307/30034902
Facione, P. A. (2013). Critical thinking: What it is and why it counts. Millbrae: Measured Reasons and The California Academic Press. https://www.law.uh.edu/blakely/advocacy-survey/Critical%20Thinking%20Skills.pdf
Fisher, A. (2001). Critical Thinking: An Introduction (Fisrt edition). Cambridge: University Press. https://assets.cambridge.org/97805210/09843/sample/9780521009843ws.pdf
Garfield, J., & Gal, I. (1999). Assessment and statistics education: Current challenges and direction. International Statistical Review, 67(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-5823.1999.tb00377.x
Greer, B. (2000). Statistical thinking and learning. Mathematical Thinking and Learning, 2 (1-2), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327833MTL0202_1
Harper, S. R. (2004). Take Time For Action: Students' Interpretations of Misleading Graphs. Mathematics teaching in the middle school, 9(6), 340-343. https://doi.org/10.5951/MTMS.9.6.0340
Jansen, A., & Spitzer, S. M. (2009). Prospective middle school mathematics teachers’ reflective thinking skills: Descriptions of their students’ thinking and interpretations of their teaching. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 12(2), 133-151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-009-9099-y
Manchester, P. (2002). The lunchroom project: A long-term investigative study. Teaching Children Mathematics, 9(1), 43-47. https://doi.org/10.5951/TCM.9.1.0043
McClain, K., Cobb, P. (2001). Supporting students' ability to reason about data. Educational Studies in Mathematics 45, 103–129. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013874514650
Medeni, T. D., & Medeni, I. T. (2012). Reflection and refraction for knowledge management systems. International Journal of eBusiness and eGovernment Studies, 4(1), 55-64. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/257135
Pagano, M., & Roselle, L. (2006). Think piece study abroad ISL: Connecting and experience. (Paper prepared for the connecting knowledge and experience conference). Elon University. https://org.elon.edu/intworkshop/document/Think%20Piece%20Study%20Abroad%20ISL2.pdf
Pagano, M., & Roselle, L. (2009). Beyond reflection: Refraction and international experiential education. Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad, 18(1), 217-229. https://doi.org/10.36366/frontiers.v18i1.263
Park, J. Y., & Kastanis, L. (2009). Reflective learning through social network sites in design education. International Journal of Learning, 16(8), 11-22. https://eprints.qut.edu.au/29596/1/29596_-_Reflective_Learning_through_Social_Network_Sites.pdf
Park, J. Y., & Son, J. B. (2011). Expression and connection: The integration of the reflective learning process and the public writing process into social network sites. MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 7(1), 170-178. https://jolt.merlot.org/vol7no1/park_0311.pdf
Plymouth University. (2010). Critical Thinking: What is critical thinking?. Learning Development with Plymouth University. https://www.hss.iitb.ac.in/sites/default/files/2023-10/Critical_Thinking%20%28Plymouth%20University%29.pdf
Prayitno, A., Sutawidjaja, A., Subanji, S. & Muksar, M. (2014). Construction theory of critical thinking as process towards refraction thinking in mathematics. In Proceedings of International Seminar on Mathematics Education and Graph Theory (pp. 10-16). Malang: Islamic University of Malang. Prayitno, A., Sutawidjaja, A., Subanji, S. & Muksar, M. (2014). Konstruksi teoritik tentang berpikir reflektif sebagai awal terjadinya berpikir refraksi dalam matematika. In Prosiding Konferensi Nasional Matematika (KNM) XVII (pp. 394-404). Surabaya: ITS.
Schon, D. A. (1991). Educating the Reflective Practitioner: Toward a new design for teaching and learning in the professions. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. http://www.thecommonwealthpractice.com/reflectivepractitionerreview.pdf
UNCMSE. (1997). Teach-Stat activities: Statistic investigations for grade 3-6. Palo Alto: Dale Seymour Publication.
Van de Walle, J. A., Karp, K. S., & Bay-Williams, J. M. (2006). Elementary and middle school mathematics. London: Pearson Education UK.
Copyright (c) 2024 Anton Prayitno, Febi Dwi Widayanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














